
Inner hyperlinks on a web site are a essential natural rating issue for Google. Hyperlinks assist Google each uncover pages and assign rankings primarily based on amount and placement. A web page with 100 inside hyperlinks is presumably a better precedence than one with a single hyperlink.
However neither function — discovery and rankings — is feasible if Googlebot can not crawl the hyperlinks. This could happen in three main methods:
- Hyperlinks behind JavaScript. Google can normally crawl and render hyperlinks in JavaScript, reminiscent of tabs and collapsible sections. However not all the time, particularly if the JavaScript requires execution first.
- Hyperlinks current on a desktop model however not on a cellular. Google indexes a web site’s cellular model by default. Nonetheless, cellular websites are sometimes downsized desktop variations with a lot fewer hyperlinks, stopping Google from discovering and indexing these excluded pages.
- Hyperlinks with a nofollow attribute or meta tag. Google claims it may observe hyperlinks with nofollow attributes, however there’s no method to know if that occurred. And the meta tag blocks crawls provided that Googlebot responds to it. Furthermore, many web site house owners are unaware of energetic nofollow attributes or meta tags, particularly in the event that they use a plugin reminiscent of Yoast, which provides these features with a single click on.
Even when a web page is listed, you possibly can by no means make sure the hyperlinks to or from that web page are crawlable and thus go hyperlink fairness.
Listed below are 3 ways to make sure Googlebot can crawl hyperlinks in your web site.
Instruments to Examine Hyperlinks
Google’s textual content cache. The text-only model of Google Cache represents how Google sees a web page with CSS and JavaScript turned off. It’s not how Google indexes a web page, as it may now perceive these pages as people see them.
Thus a web page’s textual content cache is a stripped-down model. Nonetheless, it’s essentially the most dependable method to inform if Google can crawl your hyperlinks. If these hyperlinks are within the text-only cache, Google can crawl them.
Past text-only, Google Cache accommodates the listed model of a web page. It’s a useful approach of figuring out lacking components on the cellular model.
Many search optimizers ignore Google Cache. That’s a mistake. All important rating components are there. There’s no different approach to make sure Google has that key data.
To entry any web page’s text-only model of Google Cache, search Google for cache:[full-URL] and click on “Textual content-only model.”
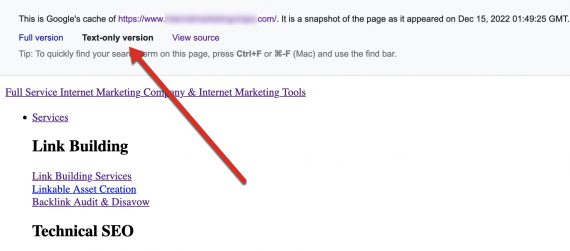
To entry the text-only model of Google Cache, search Google for cache:[full-URL] and click on “Textual content-only model.” Click on picture to enlarge.
—
Not all pages will seem in Google Cache. If a web page is absent, use “Examine URL” in Search Console or browser extensions for particulars on how Google renders it.
‘URL Inspection’ in Search Console exhibits any web page as Google understands it. Enter the URL after which click on “View crawled web page.”
From there, copy the HTML that Google makes use of to learn the web page. Paste that HTML in a doc reminiscent of Google Docs and search (CTRL+F on Home windows or CMD+F on Mac) for the linking URLs you’re verifying. If the URLs are within the HTML code, Google can see them.
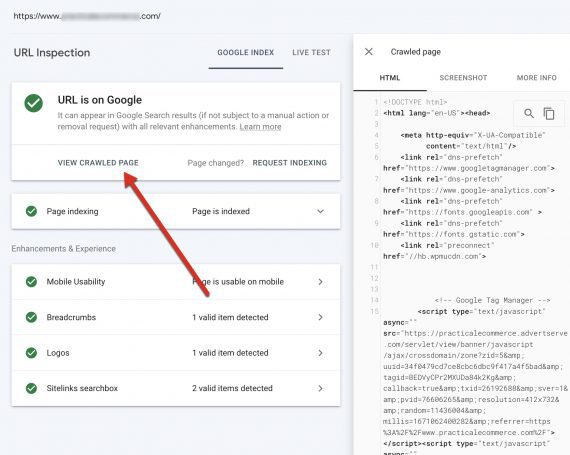
‘URL Inspection’ in Search Console exhibits any web page as Google understands it. Enter the URL after which click on “View crawled web page.” Click on picture to enlarge.
Browser extensions. When you affirm Google can see the hyperlinks, be certain that they’re crawlable. Reviewing the code will determine each the nofollow attribute and the meta tag. Firefox has a local software to load a web page’s HTML through CTRL+U on Home windows and CMD+U on Mac. Then seek for “nofollow” within the code.
The NoFollow browser extension — out there for Firefox and Chrome — highlights nofollow hyperlinks as a web page masses — in an attribute and a meta tag.
Not Definitive
None of those strategies definitively informs whether or not the hyperlinks affect rankings. Google’s algorithm is extremely subtle and assigns which means and weight to hyperlinks because it chooses, together with ignoring them. Nonetheless, accessing and crawling hyperlinks are Googe’s first step.